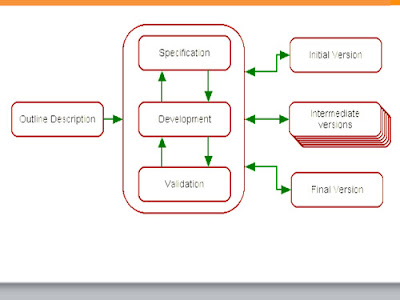
The Rational Unified Process Model

Rational Unified Process: The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable process framework, intended to be tailored by the development organizations and software project teams that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs. RUP is a specific implementation of the Unified Process. •Inception The primary objective is to scope the system adequately as a basis for validating initial costing and budgets. In this phase the business case which includes business context, success factors (expected revenue, market recognition, etc.), and financial forecast is established. To complement the business case, a basic use case model, project plan, initial risk assessment and project description (the core project requirements, constraints and key features) are generated. After ...